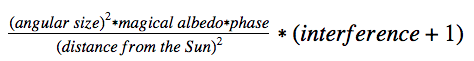Astronomy Class Notes - Year 1
written by Ivy GreenBriar
All of my Astronomy Notes as a First Year Ravenclaw Student
Last Updated
12/12/22
Chapters
4
Reads
589
Lesson 5: A.M.E. in Depth
Chapter 4
- Distance from the sun:
- Amount of sun an object receives from the sun varies with the inverse of the square of its distance from the sun
- The sun's light spreads out over a larger area the further it travels
- Angular Size
- Size of an object seen by an onserver
- Not the actual physical size measured in miles or kilometers
- Measured via an angle
- Greatest angular separation between two ends of an object
- Bigger the angular size, the more light it sends to the earth
- Albedo
- Ratio of the light reflected off the surface to that incident on, or hitting, the surface
- Ideal surface reflecting no light would have an albedo of 0
- Ideal surface reflecting all light would have an albedo of 1
- Examples:
- Dry sand reflects 40% of light resulting in an albedo of 0.4
- Snow reflects 90% of light resulting in an albedo of 0.9
- Magnesium oxide reflects 96% of light resulting in an albedo of 0.96
- Black velvet reflects 1% to 3% resulting in an albedo of 0.01 to 0.03
- Phase
- Can be described by a number between 0 and 1
- Proportion of the body that is lit in the sky
- Dr. Mansour's Contribution
- Magical Albedo vs Optical Albedo
- Light-colored objects reflect more magic
- Magic can pass through clouds and walls easily
- Interference
- Constructive interference occurs when reflection from two or more magical sources enhance each other so that the magic reflected from each is stronger then normal
- Destructive interference occurs when two or more reflections partly or completely cancel each other out
- Objects that appear to be 90 degrees apart do not interfere
- Closer then 90 degrees interfere constructively
- Further then 90 degrees interfere destructively
- Magical Albedo vs Optical Albedo